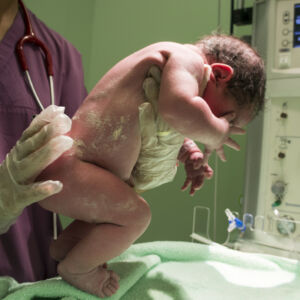
Paediatrics is a branch of medicine concerned with the study, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of childhood diseases.
NEONATOLOGY
Neonatology (also known as paediatrics or neonatal medicine) is the branch of medicine concerned with the care of newborn babies and children up to one year of age.
Neonatology focuses on the assessment, treatment and prevention of disorders in infants from birth to the first two months of life.
Neonatal care involves a wide range of medical interventions, including:
- Tube feeding (enteral nutrition) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN), if indicated:
- Ventilation support;
- Respiratory support;
- Circulatory support;
- Life-saving support;
- Diagnosis and treatment of infections such as sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia and others;
- Diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart disease;
INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Paediatric infectious diseases (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) are a medical speciality that deals with infectious diseases of the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinary tracts in infants, children and adolescents.
In general, paediatric infectious diseases can be divided into those that are specific to childhood, such as streptococcal pharyngitis or viral hepatitis, and those caused by infectious agents found only in adults.
Viral hepatitis is a group of diseases caused by different viruses. The most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, B and C.
Hepatitis A is usually a mild illness that lasts a few weeks. Hepatitis B can cause serious illness, including liver failure and death.
Hepatitis C can cause symptoms similar to other types of viral hepatitis, but it can also cause chronic infection without symptoms.
Some people with chronic hepatitis C develop serious health problems, such as cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) or liver cancer.
METABOLIC DISORDERS
Metabolic disorders in children (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) include a wide range of conditions resulting from abnormalities in the metabolism of lipids, amino acids and carbohydrates.
Metabolic disorders are diagnosed on the basis of the nature and severity of symptoms, physical observations and the results of blood tests and other diagnostic tests.
Metabolic disorders can be congenital or acquired, but in most cases genetic transmission plays an important role. These disorders have many similarities and can be grouped together as metabolic diseases.
Childhood metabolic diseases include:
Diabetes mellitus, which is characterised by high blood sugar levels caused by a deficiency or lack of insulin, an hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
Hypothyroidism, which is caused by an underactive thyroid gland. A person with hypothyroidism has too little thyroid hormone in their body and may experience symptoms such as weight gain, frequent fatigue, dry skin, hair loss, and joint and muscle pain.
Hyperthyroidism, which is caused by an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism). A person with hyperthyroidism has too much thyroid hormone in their body and may have symptoms such as weight loss, nervousness or anxiety, tremors, heavy sweating and difficulty sleeping.


ADOLESCENT MEDICINE
Adolescent medicine is the branch of paediatrics that focuses on the physical and mental health problems of adolescents.
It aims to help young people have healthy lifestyles, be physically active and make good decisions about issues that are important to their lives.
The goal of adolescent medicine is to ensure that all adolescents have access to quality health care throughout their lives.
This includes preventive care (such as immunisations), diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic illnesses, management of behavioural problems, and management of psychosocial aspects of illness such as depression or addiction, and supporting the transition to adulthood by planning for adult health care needs.
WHAT IS BRONCHIOLITIS IN BABIES?
Bronchiolitis (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) is an infection of the airways that causes symptoms such as coughing, wheezing and difficulty breathing. It is usually caused by infection with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), but it can also be caused by other viruses and bacteria.
In babies under two months old, bronchiolitis can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia and sepsis. It is rarely serious in older children, but can be very distressing for parents.
The main symptoms of bronchiolitis are:
- Coughing and wheezing – these symptoms may get worse at night
- Difficulty breathing – your child may be able to get enough air when sitting or lying down, with the head slightly raised from the chest. However, he or she may not be able to breathe properly when lying on his or her back or sitting upright.
- Irritability and fever – your child may feel unwell and have a high temperature (fever) of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher.
WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC EMERGENCIES?
Paediatric emergencies are conditions that require immediate attention. They can be life-threatening or cause serious complications if not treated immediately.
What is a paediatric emergency?
A paediatric emergency is a condition that requires immediate medical attention. The need for fast assistance can come from a number of sources, including:
- Loss of consciousness
- Severe bleeding or bruising
- Burning or smoke inhalation
- Convulsions and fits (seizures)
- Poisoning, including prescription medicines or household chemicals
- choking on an object that does not pass naturally through the windpipe (trachea such as food or a toy) or complete throat blockage by a stuck object (such as a coin).
We present to you some articles relating to pathologies treated in our Mediterranean clinic, with an effective and efficient medical and paramedical team.
Chickenpox (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) is a contagious disease caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV). It causes a rash of small red spots that itch and blister, usually on the face and torso. After a few days, the spots turn into blisters filled with fluid. The blisters turn into crusts and fall off after three to four weeks. Chickenpox is generally considered to be a rarely serious childhood illness. However, it can be dangerous for people with weakened immune systems, especially if they catch it at a young age or have other health problems.
Symptoms of chickenpox:
Chickenpox occurs in two stages: primary infection (when you are first infected) and reactivation (when the virus reappears).
During the primary infection:
You may feel ill for two to four days, with fever, chills and headache, before your skin starts to blister. You will also have itching all over your body. This stage lasts six to ten days before the rash appears. The outbreak is in the form of small red bumps that quickly turn into blisters that contain fluid and fill with pus. After three or four days, these blisters open up and turn into crusts, which finally turn into brown crusts that fall off after about a week.
Measles, also known as rubella or morbilla, is a highly contagious viral disease. It is characterised by a generalised rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. Other common symptoms include fever, runny nose, red eyes and small white spots in the mouth. In rare cases, measles can cause blindness or encephalitis in an infected person.
Measles is caused by an RNA virus of the genus Morbillivirus in the family Paramyxoviridae. There are a number of vaccines that can prevent measles, including MMR (measles-mumps-rubella), RotaTeq (rotavirus), Varivax (varicella), MMRV (measles-mumps-rubella-varicella) and ProQuad (measles-mumps-rubella-varicella).
Measles is highly contagious; 90% of non-immune people exposed to measles will become infected with the virus. The virus is spread by inhaling airborne droplets from an infected person who sneezes or coughs, by direct contact with secretions from the nose and mouth, or by contact with contaminated objects such as doorknobs.
Mumps (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) is a contagious disease caused by the mumps virus. The virus is spread through saliva or mucus in the mouth, nose or throat of an infected person.
Mumps is highly contagious and spreads quickly between people who live close to each other. It is spread when droplets of saliva or mucus from the mouth, nose or throat of an infected person (for example, from coughing or sneezing) fall into the mouth or nose of another person.
The mumps virus can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy or birth. This can cause serious problems for the baby.
The symptoms
The symptoms of mumps usually appear 16 to 18 days after infection:
- Fever
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle pain (myalgia) and jaw pain (temporomandibular joint pain)
- Swollen glands under one or both ears (parotitis), which may be tender.
Diarrhoea is the passing of loose or liquid stools more than three times a day. Diarrhoea can be caused by many different things. The most common causes of diarrhoea in children are viruses, bacteria and food allergies.
Diarrhoea is one of the most common childhood illnesses. It is important to know the signs and symptoms so that you can act as quickly as possible, especially if your child is dehydrated.
Symptoms of diarrhoea in children:
Liquid stools: This can be caused by viruses, bacteria or food allergies.
Frequent urination: Your child may urinate more often than usual, and the urine may be darker in colour than normal urine.
Vomiting without diarrhoea: Sometimes vomiting occurs without diarrhoea, leading to dehydration (lack of water in the body).
Dehydration: Dehydration can occur when your child loses too much water in their body because they have vomited or had diarrhoea for a long time without drinking enough fluids to replace what they lose through urination and sweating. If not treated immediately, dehydration can become serious and life-threatening if it lasts more than 12 hours.
Pneumonia (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department) is an infection of the lungs. It can be caused by a virus, bacteria or fungus.
Pneumonia is more common in children under 5 and adults over 65. It is also more common in people with chronic lung diseases, such as asthma or emphysema, and in people with a weakened immune system.
Pneumonia causes a cough with phlegm (sputum), fever and shortness of breath.
Symptoms are often sudden and may include:
- High temperature (fever), equal to or greater than 100.4°F (38°C)
- Coughing up greenish-yellow mucus (sputum) that may be tinged with blood
- Rapid breathing or difficulty in breathing
- Muscle weakness, especially of the chest wall muscles during inhalation (called pleuritic chest pain)
You ask, our teams answer.
F.A.Q
Paediatricians are doctors who look after children from birth to adulthood. A paediatrician is a primary care doctor, just like an adult family doctor or general practitioner.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) defines paediatrics as “the branch of medicine concerned with the health, diseases and disorders of infants, children and adolescents”.
Paediatrics is a medical speciality that focuses on the physical and mental development of children from birth through early adolescence. Paediatricians specialise in childhood diseases and disorders, including common ailments such as colds and ear infections, as well as more serious problems such as cancer and congenital deformities.
Paediatricians also vaccinate against infectious diseases such as measles and polio, advise parents on health issues such as diet and nutrition, screen newborns for genetic abnormalities or birth defects, and treat chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus.
Sepsis (take in charge in our Paediatrics Department), also known as septicaemia and blood poisoning, is a condition that occurs when an infection affects the body. Symptoms include a raised temperature, rapid breathing and a fast heart rate. In severe cases, organ failure can occur.
The most common cause of sepsis is bacterial infection, but it can also be caused by fungi or viruses. Sepsis can be localised (such as pneumonia) or systemic, affecting the whole body (septic shock).
Treatment for sepsis includes antibiotics, fluids and oxygen therapy to reduce low blood pressure. It also involves close monitoring of the patient’s vital signs and organ function.
The branch of medicine that deals with the care of newborn babies. The neonatal period is defined as the first 28 days after birth.
Neonatology is the branch of medicine that deals with newborn babies and the management of their initial health problems. The term is derived from neo (new) and natus (born). It is also known as perinatology. The neonatal period is from birth to 28 days after birth, and neonatologists are doctors who specialise in this age group.
Neonatologists work in hospitals as well as clinics, where they can provide advice and referrals for high-risk pregnancies. Babies born prematurely (before 37 weeks gestation) are at risk of developing chronic health problems such as cerebral palsy or mental retardation later in life. Neonatologists therefore have a great need for specialised care for these children in the first few months of life.
Depression (treated in our paediatric department) is a mental health condition characterised by a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. It affects the way you think, feel and behave. Depression can affect your self-esteem, your relationships and your ability to enjoy life. But it can be treated with the help of your doctor or therapist.
Signs and symptoms of depression:
People with depression may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
– Feeling hopeless, helpless or worthless most of the time.
– Feeling sad, anxious or empty.
– Lack of energy, feeling like you are dragging yourself through life.
– Loss of interest in things you used to enjoy (work, hobbies, social relationships).
– Changes in appetite or sleep (frequent) – eating too much or not being able to eat enough; sleeping too much or having insomnia (difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep); waking up early in the morning and feeling tired all day.
– Difficulty concentrating on something for a long period of time.