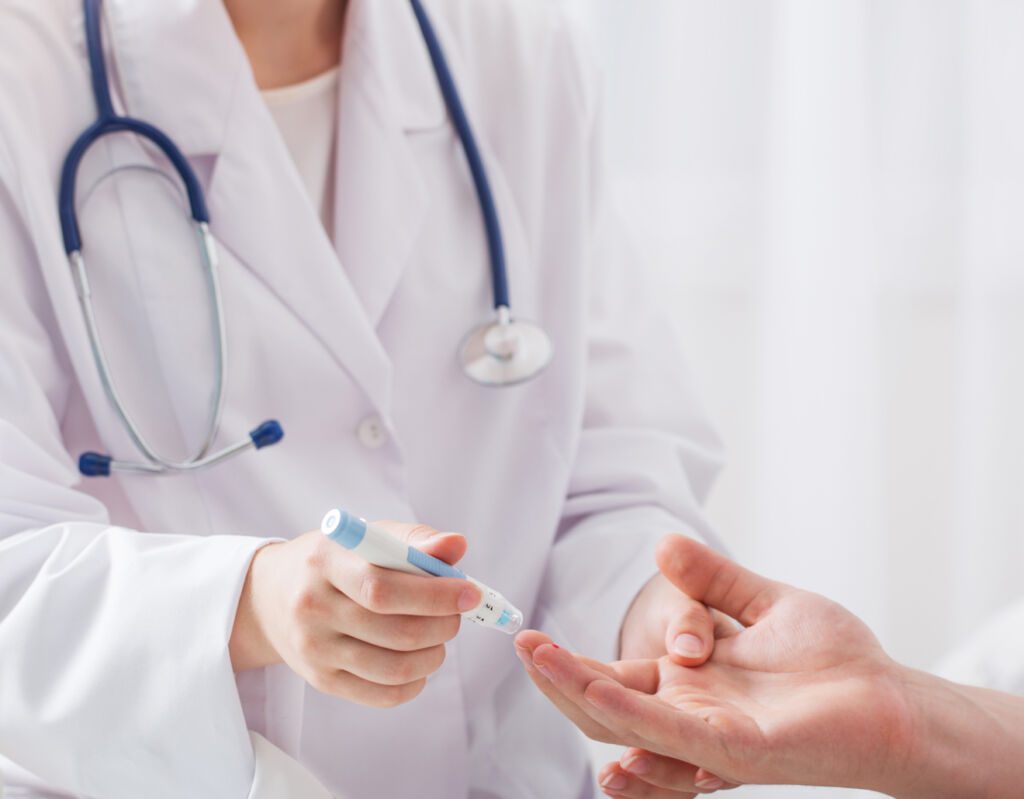
DIABETES TREATMENT
There are three main types of diabetes (treated in our Endocrinology and Diabetology department):
Our medical teams treat the different types of diabetes
– Diabetes Type 1, which often appears in childhood
– Gestational diabetes, which appears during pregnancy and often disappears after childbirth;
– Diabetes Type 2, the most common form of diabetes, which appears in adulthood.
Diabetes treatment aims to control blood glucose levels, prevent complications and improve quality of life. Diabetes treatment may include:
- A healthy diet that includes counting carbohydrates and regular physical activity
- Medication to control blood glucose levels, including insulin injections for people with type 1 diabetes
- Insulin therapy for people with type 2 diabetes who cannot control their blood glucose levels with diet and exercise alone.

OBESITY
Obesity (treated in our Endocrinology and Diabetology department) is a pathological condition characterised by the accumulation of excess body fat to the point where it can have a negative impact on health. An obese person has a body mass index (BMI) – measured by weight in relation to height – of over 30 kg/m2.
Obesity can significantly increase the risk of many chronic diseases and conditions, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension (high blood pressure) and osteoarthritis.
The most common medical treatment for obesity is bariatric surgery. A bariatric surgeon removes part of the stomach (sleeve gastrectomy) or bypasses the intestines (gastric bypass). Gastric banding is another option, but does not require general anaesthetic as gastric bypass does.
Bariatric surgery can help you lose about 30% of your excess weight within a year, depending on the procedure chosen and the amount of weight you want to lose.
WHAT IS DIABETIC FOOT?
The diabetic foot (treated in our Endocrinology and Diabetology Unit) is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition that can lead to amputation if left untreated. It occurs when small blood vessels in the foot are damaged or destroyed, which can lead to infection of the bone or tissue around the toes, heel and ankle.
Symptoms of diabetic foot include:
- Redness or swelling in the affected area.
- Pain in the foot, ankle or heel.
- Limping when walking.
- White patches on the toenails.
- Sensitivity to pressure in certain areas of the foot.
The term “diabetic foot” is used to describe a number of problems that can occur in the feet of people with diabetes. Some of these problems may include:
- Thickening of the skin (called diabetic dermopathy).
- Numbness and tingling.
- Calluses or corns.
- Skin ulcers that don’t heal.
WHAT IS GESTATIONAL DIABETES?
Gestational diabetes (treated in our Endocrinology and Diabetology department) is a type of diabetes that first appears during pregnancy. It is usually temporary, i.e. it disappears after the baby is born. But if you have gestational diabetes, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
– What is gestational diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) that occurs in women who have never had diabetes before and who are not obese. Gestational diabetes usually disappears after the baby is born.
– What causes gestational diabetes?
The cause of gestational diabetes is unclear, but research suggests that hormones produced by the placenta may affect insulin production. Researchers are trying to understand the causes of these hormonal changes so that they can be prevented or treated with drugs or other therapies.
We present to you some articles relating to pathologies treated in our Mediterranean clinic, with an effective and efficient medical and paramedical team.
The endocrine system is very important for the proper functioning of the body. However, sometimes hormones are disrupted and cause imbalances.
Considering the gastric band procedure for weight loss? This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about the surgery, risks and benefits.
You ask, our teams answer.
F.A.Q
Diabetology is the branch of medicine concerned with the study, treatment and prevention of diabetes mellitus. It is also known as endocrinology. It is a specialty that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases in which blood glucose levels are high over a long period of time. There are two main types of diabetes: diabetes type 1, sometimes called insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), and diabetes type 2, sometimes called non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). The vast majority of people with diabetes have diabetes type 2.
In addition to regulating blood glucose levels, insulin also regulates protein and fat metabolism. Insulin receptors are found in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver and heart muscle. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease has been debated for many years, but it appears to play a major role in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
The first-line treatment for both types of diabetes is diet and exercise. Oral medications can be used for long periods to help control blood glucose levels.
Diabetes Type 2 is a condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy. In diabetes type 2, either the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin, or the cells don’t respond properly to insulin. As a result, glucose cannot enter the cells and builds up in the bloodstream.
Diabetes Type 2 used to be known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) or adult-onset diabetes. It usually develops in people over the age of 40, although it can occur at any age. In fact, about 10% of children and adolescents have diabetes type 2.
Treatment consists of lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, weight loss if necessary and physical activity most days of the week. Some people may also need medication to control their blood glucose levels.