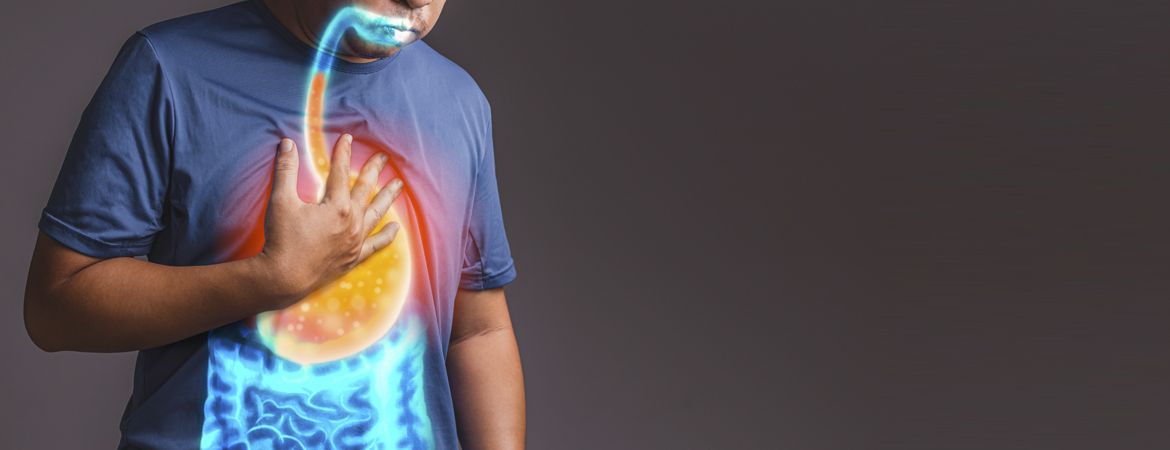
Whether in Tunis or elsewhere, more and more people are suffering from digestive diseases. The main causes are obesity, overweight, drug use, excessive alcohol consumption and poor diet. To find out more about these diseases, let’s take a closer look at the field of gastroenterology and hepatology.
DEFINITION OF GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
To understand the causes, symptoms and treatments of digestive diseases, you’ll need to take a closer look at gastroenterology and hepatology.
By definition, gastroenterology is a medical specialty that studies, diagnoses and treats diseases of the digestive system. These diseases can affect the digestive tract, including the oesophagus, stomach, intestines, colon and rectum.
Hepatology is a branch of gastroenterology. It deals with the treatment of diseases of the liver and bile ducts.
THE ROLE OF THE GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Now that we’ve seen the definition of gastroenterology and hepatology, let’s look at the role of the gastroenterologist. A gastroenterologist is a specialist who treats all diseases of the digestive system, pancreas and liver.
More specifically, he or she will interview and examine patients to diagnose digestive diseases. He or she will then suggest appropriate treatment.
For treatment, he or she may carry out various endoscopic procedures. These include colonoscopy, upper endoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, barium enema, cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound.
If you have a serious digestive condition, you should see a gastroenterologist immediately. You can also see a general practitioner first. He or she will refer you to a gastroenterologist for further investigation.
THE ROLE OF THE HEPATOLOGIST
Like the gastroenterologist, the hepatologist practices gastroenterology. However, the hepatologist’s role is more in-depth. In fact, he is more competent in the treatment of hepatobiliary diseases. These are diseases of the liver and its appendages, the bile ducts and the gallbladder.
He can treat acute, chronic or minor diseases. Children and adults are welcome.
A hepatologist’s main role is to diagnose and treat liver disease when referred by a referring doctor. For diagnosis and treatment, this specialist will see patients and carry out a clinical examination. He/she may also carry out specific investigations or order additional tests.
Once a precise diagnosis has been made, the specialist will suggest a range of treatments, depending on the case. These may include endoscopy, antiviral treatment, surgery, chemotherapy and liver transplantation.
Follow-up examinations are then carried out to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and the progress of the disease. Finally, the hepatologist will make an assessment before and after a liver transplant, if necessary.
The hepatologist is also involved in the management of addiction to illicit substances and alcohol, which are bad for the liver. He also offers therapeutic education to reduce risk, palliative care and clinical trials.
SOME DISEASES TREATED
As mentioned above, gastroenterology and hepatology treat diseases of the digestive system, liver and bile ducts. Here are some examples of conditions that a gastroenterologist and hepatologist may treat.
CONSTIPATION
Constipation is when you have more difficulty than usual passing stools. This is often a temporary condition and can be treated by a general practitioner. However, if it’s a recurring problem, it’s best to see a gastroenterologist.
DIARROHOEA
Everyone has had diarrhoea. It’s when you have loose stools and need to go to the toilet several times a day. It’s usually not serious. However, if the diarrhoea persists, if you have unusual pain, or if the stools contain traces of blood, you should see a gastroenterologist.
STOMACH ULCER
This is a lesion of the first part of the intestine, called the duodenum, or a lesion of the stomach wall. Peptic ulcers are caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. See a gastroenterologist to control this bacterium.
CROHN’S DISEASE
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the bowel. Crohn’s disease can affect the entire digestive tract. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, burning or anal pain. You may also experience loss of appetite, chronic diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting.
It is advisable to see a gastroenterologist to analyse these symptoms and treat the condition.
ACUTE PANCREATITIS
This is inflammation of the pancreas. It can be severe or mild. It is often caused by alcohol abuse or gallstones. What are the symptoms? You may have pain in your back and upper abdomen, vomiting, nausea or diarrhoea with pale stools. Whatever the cause, you should see a gastroenterologist or hepatologist for appropriate treatment.
CHRONIC PANCREATITIS
Pancreatitis is called chronic when there is a persistent inflammation of the pancreas. Over time, this can lead to scarring or lesions. The cause is the same as for acute pancreatitis. Symptoms include abdominal pain, especially when eating or drinking. There may also be tiredness, weight loss or yellowing of the skin.
If you notice any of these symptoms, don’t hesitate to see a hepatologist or gastroenterologist.
CIRRHOSIS
Liver cirrhosis is a serious liver disease. It is mainly caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It can also be caused by hereditary liver disease or the hepatitis C virus.
Because it is so serious, it can lead to liver cancer or liver failure. Cirrhosis is often asymptomatic. Symptoms don’t appear until the disease has reached an advanced stage. You may have a feeling of heaviness in your stomach. You may also have itching or greasy stools.
You may also lose weight or your appetite. It is advisable to see a hepatologist for any treatment.

