Understanding ultrasound: a comprehensive guide.
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique commonly used to visualise the body’s internal organs and tissues. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn everything you need to know about ultrasound, from how to prepare for a scan to how to interpret the results.
We also look at the different types of ultrasound available and why they are used.
WHAT IS ULTRASOUND?
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal organs and tissues.
It is non-invasive, meaning it does not require an incision or anaesthetic, and is generally considered to be safe and painless.
The images produced by ultrasound can help doctors diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
There are different types of ultrasound:
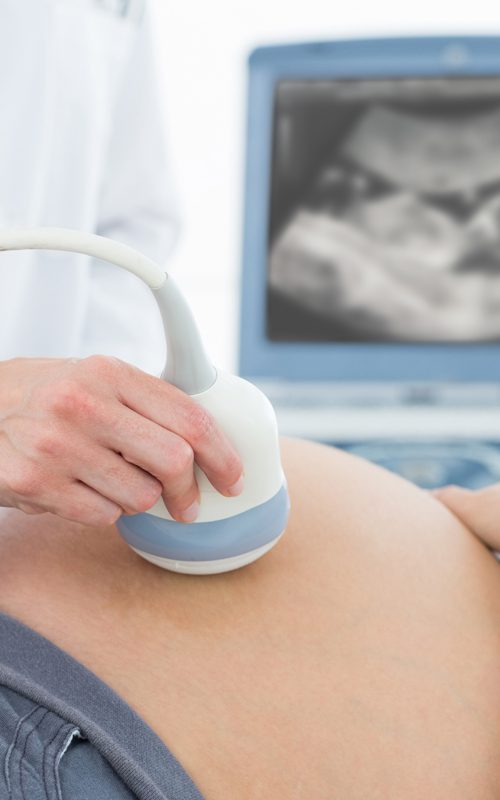
– Pregnancy Echography:
Pregnancy Echography is used to check the development of the foetus, monitor potential complications and assess the health of the foetus. Ultrasound may also be used to guide procedures such as needle biopsies.
– Pelvic ultrasound:
Echography is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In women, Echography can be used to assess the endometrial mucosa of the uterus (internal endometrial echo) and ovarian cysts (ovarian echo). It can also be used to examine the fallopian tubes and ovaries if infertility is suspected.
In men, Echography can be used to check the prostate for abnormalities such as cancerous tumours (prostate echo). Ultrasound can also be used to guide the placement of needles during prostate or kidney biopsies.
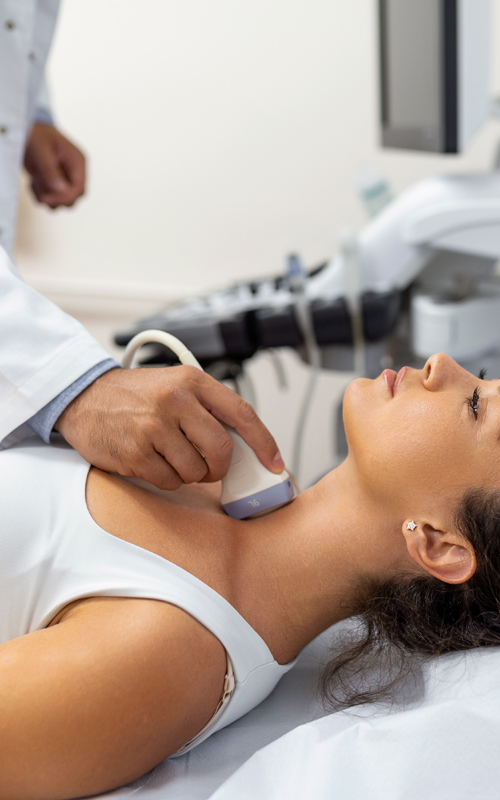
– Neck ultrasound:
The images produced by a neck Echography can help doctors diagnose conditions such as: tumours, cysts, inflammation or infection, and especially the proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
– Morphological Echography can help doctors diagnose many types of conditions, including:
- Abnormalities of muscle tone (spasticity)
- Fetal abnormalities
- Abnormalities of the heart and arteries
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease)
- Kidney stonesE
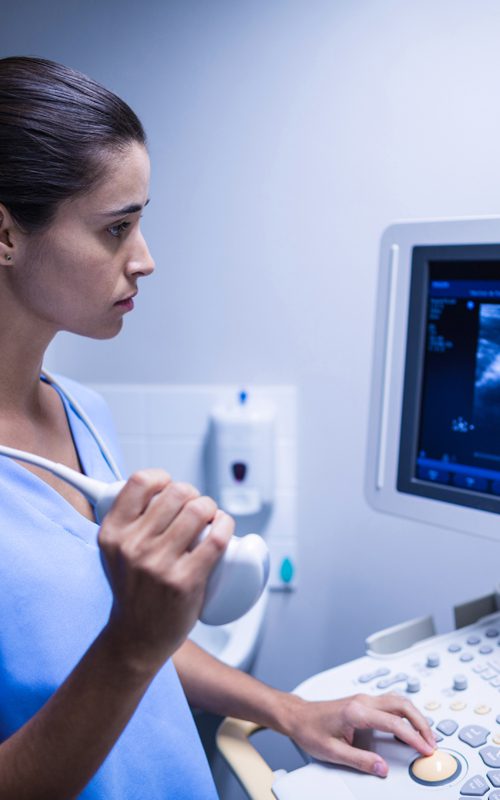
HOW SHOULD I PREPARE FOR AN Echography SCAN?
Before having an ultrasound scan, it is important to prepare properly to ensure that the results are as accurate as possible. Firstly, it is important to follow the preparation instructions given to you by your doctor or Echography technician. This may include instructions on what to eat or drink before the test and what to wear. It is also important to inform your doctor about any medication you are taking, as some medicines can affect the results of an Echography scan. Finally, it is important to relax and stay calm during the scan to help get clear and accurate images.
HOW AN Echography TAKES PLACE?
An ultrasound is a non-invasive medical test that uses sound waves to create images of the body’s internal organs. During the test, you will lie on a table and a gel will be applied to the area to be examined. The Echography technician will then use a transducer, a small device that emits sound waves, to take images of the area being examined. The scan can take anywhere from a few minutes to an hour, depending on the area being examined. You can return to normal activities immediately after the test. Your doctor will review the Echography results and inform you of the next steps to follow.
HOW ARE THE ULTRASOUND RESULTS INTERPRETED?
The interpretation of the ultrasound results is usually performed by a radiologist or a doctor who specialises in medical imaging. The results are presented in the form of images and a written report. The images may be in black and white or colour, depending on the type of ultrasound performed. The written report will include information about the structures examined, any abnormalities and the radiologist’s or doctor’s conclusions. It is important to discuss the results with your doctor to understand what they mean for your health and what the next steps should be.
BENEFITS AND LIMITATIONS
Ultrasound is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the body’s internal organs. It has many advantages, including that it does not require exposure to ionising radiation, is relatively inexpensive and can be used to examine many different organs. However, it also has limitations, including that it can be less accurate than other imaging techniques for certain structures, can be difficult to interpret in some cases, and can be limited by obesity or gas in the bowel. It is important to discuss the benefits and limitations of ultrasound in your specific situation with your doctor.