Understanding fibroids: symptoms, causes and treatments
If you have fibroids, you know how painful and distressing this condition can be. It is important to understand the symptoms, causes and treatment options available to help you manage this condition. This guide provides useful information to help you understand fibroids and the treatment options available.
WHAT ARE FIBROIDS?
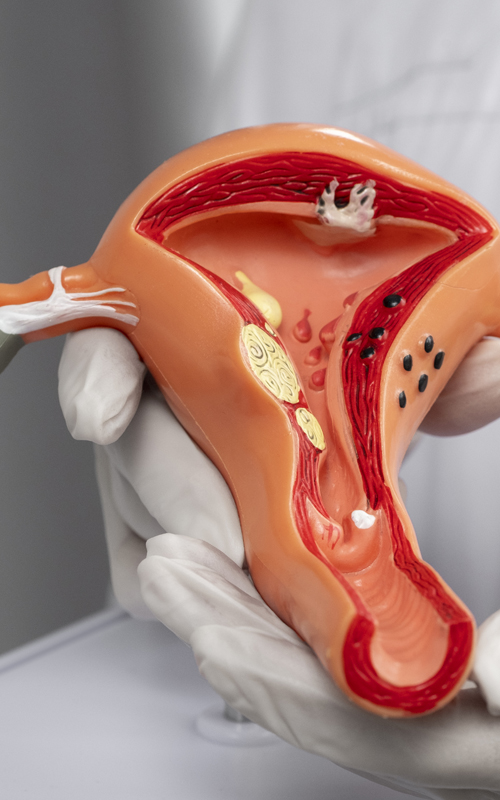
A fibroid is a benign tumour that develops in the uterus. It is also known as a myoma. Fibroids can vary in size and number, from small tumours to large masses.
It can be submucosal (under the uterine wall) or intramural (inside the uterine wall). Most fibroids are submucosal, but intramural fibroids can cause more severe symptoms because they put pressure on other organs.
There are two types of fibroid tumour: leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas.
A leiomyoma is an abnormal growth of smooth muscle cells in the uterus. Leiomyomas are also called uterine fibroids. Treatment for leiomyomas depends on their location in the uterus and the symptoms they are causing. If the leiomyomas are small and asymptomatic, surgery may not be necessary. If surgery is required, there are several options, including myomectomy (removal of the tumour), myolysis (destruction of the tumour by heat), laser ablation (destruction of the tumour by heat) or hysteroscopic resection (removal of the tumour through the cervix).
Leiomyosarcoma is a type of sarcoma that starts in the smooth muscle cells of the uterus. It can also affect other organs, including the bowel, bladder and heart.
Symptoms can include abdominal pain, heavy menstrual bleeding and pain during sex.
The exact causes of fibroids are not known, but factors such as heredity, hormones and age may play a role in their development.
COMMON SYMPTOMS
Common symptoms include abdominal pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, pain during intercourse, frequent urination, pressure in the lower abdomen and lower back pain. These symptoms can vary in intensity depending on the size and location of the fibroids. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
POSSIBLE CAUSES
The exact causes of fibroids are unclear, but they are probably caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors. They are more common in women of childbearing age and may be linked to high levels of oestrogen. Family history may also increase the risk of developing the condition. Other risk factors include obesity, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR FIBROIDS
There are several treatment options for uterine fibroids, depending on the size, location and number of fibroids, as well as the patient’s overall health. Treatment options include regular monitoring, medication to reduce symptoms, hormone therapy, surgery to remove the fibroids or the uterus, and non-surgical procedures such as fibroid embolisation. It is important to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment option with your doctor to determine the best approach for your individual situation.
TIPS FOR MANAGING FIBROID SYMPTOMS
Symptoms of fibroids vary from woman to woman, but may include abdominal pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, pain during sex, and frequent urination. To help manage these symptoms, it is recommended to exercise regularly, eat a healthy and balanced diets, take over-the-counter painkillers for pain relief, and discuss the available medical or surgical treatment options with your doctor. It is important not to ignore the symptoms and to seek medical advice if you think you may have them.
Lifestyle changes are strongly recommended, including:
Physical activity: Regular exercise can help reduce the symptoms of fibroids by increasing the breakdown of oestrogen and reducing water retention. Exercise also helps to strengthen the abdominal muscles, which can facilitate the evacuation of urine if the uterus prolapses (see below).
Weight loss: Obesity increases oestrogen levels and promotes the growth of fibroids. Weight loss may improve symptoms caused by this pathology, such as heavy menstrual bleeding or pelvic pressure due to an enlarged uterus pressing on other organs such as the bladder or rectum (called uterine prolapse). If you are overweight or obese, ask your doctor to help you lose weight safely through a healthy diet and exercise before trying other treatments for fibroids.